The B-21 Raider: Designed For Low Risk

Images released during the week of the Air and Space Force Association’s Air, Space & Cyber Conference revealed a head-on view that allowed for a reliable estimate of the wingspan.
The design of Northrop Grumman’s B-21 Raider points to a conservative approach on the part of the U.S. Air Force’s Rapid Capabilities Office. The B-21’s resemblance to the original B-2 bomber design is close, but it is a smaller aircraft, with a wingspan estimated at 132 ft. compared with the B-2’s 172 ft., and is approximately half the empty weight. The planform itself is driven by the need to accommodate complex inlets and exhausts and a large weapon bay within the flying-wing profile while staying within a maximum thickness-to-chord ratio compatible with efficient flight above Mach 0.8.
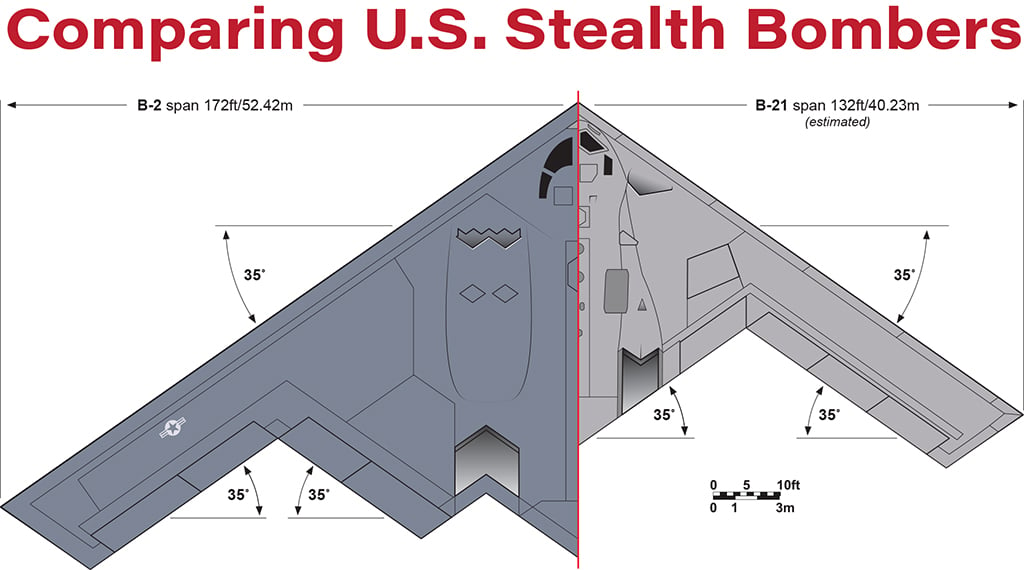
The B-21 planform, which has not been officially released, was depicted in a video that accompanied a presentation by Gen. Duke Richardson, commander of the U.S. Air Force Materiel Command, on Sept. 11 at the Air and Space Force Association’s (AFA) Air, Space & Cyber Conference at National Harbor, Maryland. A new set of images released that week included an undistorted head-on view that permitted a reliable estimate of the wingspan. Recently recovered unclassified imagery from Pratt & Whitney presentations dating back to the early 2010s proved to be a close match for the B-21’s inlets.
- U.S. Air Force Rapid Capabilities Office prioritized use of mature subsystems
- Northrop draws on aspects of B-2 bomber and X-47B UCAV
The B-21’s low-risk design in part stems from the program’s origins. Before 2009, the Air Force was working to a requirement known as Next-Generation Bomber (NGB). It has been characterized as complex and ambitious, with a full suite of intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) sensors, a self-defense capability and long endurance. This was canceled in April 2009 by then-Defense Secretary Robert Gates.
The following year, the Air Force proposed a different approach to the mission, which Pentagon leadership found acceptable: a Long-Range Strike family of systems including classified uncrewed aircraft systems for ISR and electronic attack (the former becoming the Northrop Grumman RQ-180), a replacement cruise missile (now the Raytheon AGM-181) and the Long-Range Strike-Bomber (LRS-B), for which a contract was awarded to Northrop Grumman in October 2015.
Aside from scrubbed and scaled-back requirements, the LRS-B project differed from NGB in three ways: Unit cost was a key performance parameter; two competing teams were funded through preliminary design review, which normally takes place after contract award; and management was assigned to the Air Force’s Rapid Capabilities Office (RCO). The RCO modeled its approach on the Lockheed F-117, developed using mature subsystems in a new platform so that the program could focus on applying new technology.
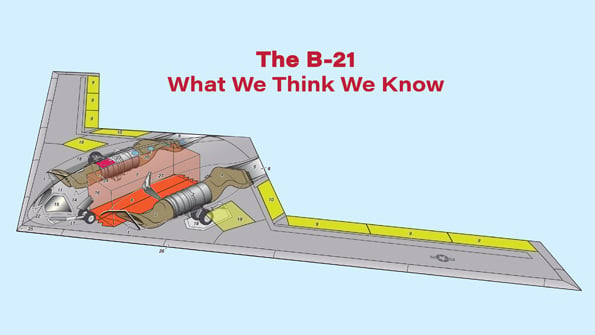
The B-21 emerging today is evidence that these principles have been adhered to. Its configuration and stealth technology have evolved from the “flying saucer” approach used on the B-2, but originally proposed in the late 1950s. Remarkably, Lockheed Martin Skunk Works founder and former chief Clarence “Kelly” Johnson, in a retrospective paper delivered in 1975 and quoting pre-SR-71 Blackbird work, noted that “a shape similar to flying saucers, with a sharp edge and no protuberances, has a very low radar cross-section without any anti-radar treatment.” And at a February 1959 conference with President Dwight Eisenhower, also discussing the future Blackbird, Harvard physicist Edward Purcell remarked that “the best shape would be a flying saucer.”
No documents found so far have explained the exact connection between the flying saucer phenomenon—the original popular term for unidentified aerial phenomena—and early stealth developments. But one part of the explanation may be that the mysterious craft were often believed to evade radar detection and that it would naturally occur to anyone with knowledge of radar that the shape might have something to do with it.
The classic 1950s flying saucer shape—seamless and continuously curved, with a domed center flaring out to a sharp edge—is visible on the B-21. Some details, though, are reminiscent of the X-47B—the uncrewed combat air vehicle (UCAV) designed by Northrop Grumman—such as the longer nose, or “beak.” This feature is a result of the need for continuous sharp leading edges, but with a curved-down nose to improve stall characteristics. As on the B-2, however, the saucer profile in elevation is matched with a straight-edge planform to concentrate residual radar reflections—reduced by deep-section radar-absorbent material (RAM) edges—in the smallest possible number of “spikes.”
The design benefits from advances in computational engineering and simulation. The B-2 was designed with the help of early 2D computational fluid dynamics (CFD), but airflows on a blended wing body shape are highly 3D with effects propagating from the center-body outward, and more recent designs using 3D CFD are more efficient.
Computational electromagnetics allows for better low radar cross-section (RCS) shapes and more efficient use of RAM and eliminates much of the empirical cut-and-try methods used in earlier programs: Northrop Grumman closed its Tejon Ranch, California, outdoor RCS test range in 2011.
The B-21 is also the first known major U.S. military aircraft program to be fully designed on a digital thread, with not only the shape but the physical characteristics of each part built into a digital prototype. This has allowed errors to be caught early and has made it possible, according to program officials, to incorporate all core systems on the first aircraft.
The differences from the B-2 include the new bomber’s planform. In fact, the B-2 planform at contract award in October 1981 was similar to the B-21’s now, but a low-altitude dash capability was added to the requirement late in its evolution. In early 1983, Northrop engineers discovered that the original design had insufficient control power to alleviate gust loads at the same time as controlling the aircraft, and it was necessary to add control area farther aft, close to the centerline, for rigidity. The fix resulted in the B-2’s unique planform, but at a price in time, weight and cost—and the low-altitude capability was never used.
Some of the features carried over from the X-47B include the apparent absence of split brake-rudder surfaces. Instead, the plan-view sketch suggests the presence of “inlay” surfaces above the wing, which would not be used in stealth mode. Instead, lateral and longitudinal control are provided by eight trailing-edge surfaces, augmented by differential thrust as on the B-2.
The center-body section matches images of highly serpentine inlets mated to a medium-bypass engine. Pratt & Whitney discussed such an engine, the PW9000, as a future bomber powerplant in 2010 but has not mentioned it since. The PW9000 used the core of the PW1000G commercial engine family, mated to a direct-drive fan with a 4:1 bypass ratio. On the B-2, the low-bypass GE F118 engine was selected because it was too risky to place a higher-bypass engine, more sensitive to flow distortion, behind the curved and RAM-treated inlet ducts needed to hide the fan face from radar. With the aid of better CFD, that problem can be eliminated: Northrop Grumman proposed a large bomber UAV in 2005, powered by two modified GE CF34 turbofans, and Lockheed Martin flew the Polecat demonstrator in 2006 with two Williams FJ44s.
Further evidence of innovation in the propulsion installation is that it is one of very few specific B-21 problem areas mentioned in public. Rep. Rob Wittman (R-Va), a member of the House Armed Services Committee, mentioned potential inlet and exhaust issues in March 2018. In March 2021, then-RCO Director Randall Walden said that a redesign was completed before the design was frozen, without affecting the schedule.
A higher bypass ratio provides much better specific fuel consumption than the B-2’s fighter-type engine, improving range, and would enable a cooler, lower-velocity exhaust, not only lowering the B-21’s infrared signature but also alleviating thermomechanical stress on the open “aft deck” area of the exhaust, immediately ahead of the trailing edge.
The B-21’s structure benefits from the absence of a low-level flight requirement and improvements in both composite materials and RAM, reducing the use of fillers and tapes. While the RAM itself would perform the same functions as on earlier stealth aircraft, with multiple layers to absorb energy, diffuse surface currents and protect the skin from lightning, it would require less maintenance than the notoriously finicky B-2 surface.
Internally, the B-21 apparently uses many proven systems. At the AFA meeting, Doug Young, Northrop Grumman vice president and general manager for strike systems, noted that where possible, the company has used commercial components and systems on the aircraft, reducing costs and taking advantage of long-lasting commercial supply networks. Early in the program, one Washington consultant with close ties to BAE Systems disclosed that the electronic warfare system of the B-21 is closely related to the Lockheed Martin F-35’s ASQ-239.
The most important feature of the avionics, however, is an open mission systems architecture. Young compares older systems with adding peripherals to a computer in the early PC age, where “you had to go through a whole rigmarole to make it work.” But the B-21 has standard interfaces and a partitioned architecture where changes to the mission systems cannot affect flight-critical functions.
The B-21 program includes a “software factory,” Young said, which is already developing capabilities beyond the service-entry baseline. And under a program called Spirit Realm, a partitioned architecture is being developed for the B-2 fleet.
After Lockheed Martin and Boeing unsuccessfully protested the Air Force’s B-21 contract award to Northrop Grumman, a consultant to both companies wrote that “there’s a real possibility that the B-21 program isn’t executable at the price the winning team bid—which would mean either big cost overruns or program termination.”
Northrop has warned that it faces up to a $1.2 billion charge on the first five years of low-rate initial production for the B-21 due to inflation-related cost increases not anticipated when bids were submitted in 2015.
But a lesson to be drawn from the B-21’s appearance is that the designers of the B-2 did an amazingly good job “inventing to schedule” while existing materials and subsystems were inadequate and produced a basic vehicle architecture that was still considered the best choice almost 40 years later.
Comments